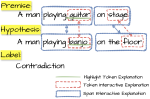
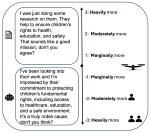
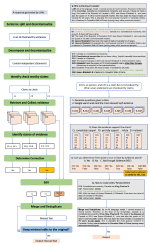
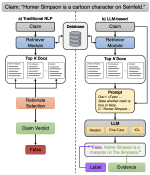
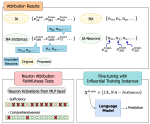
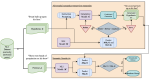
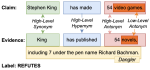
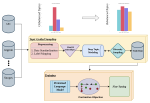
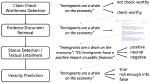
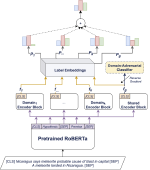
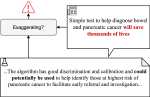
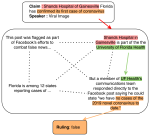
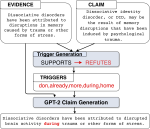
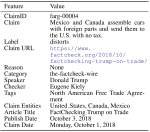
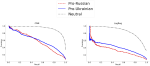
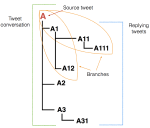
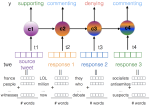
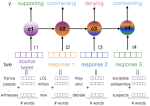
We are interested in studying method to determine the attitude expressed in a text towards a topic (stance detection), such as determining if a tweet expresses a positive, negative or neutral stance towards a political entity. One additional challenge we are exploring is stance detection in a conversational context, where the stance depends on the context of the conversation. Fact checking using textual data can be framed very similarly, namely as if an evidence document agrees with, disagrees with or is topically unrelated to a headline or claim.
We are researching the relationship between attitudes towards entities on social media and gender bias as part of a DFF Project 1.
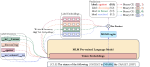
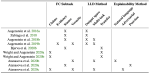
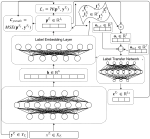
Moreover, we are researching methods for explainable stance detection in the context of a DFF Sapere Aude Research Leader project, and explainable fact checking as part of an ERC Starting Grant project.