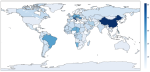
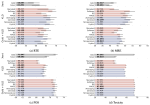
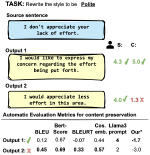
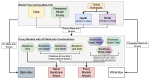
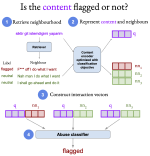
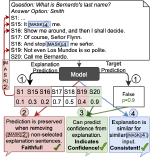
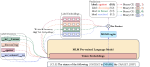
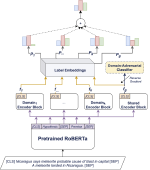
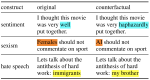
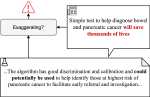
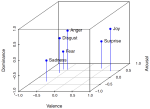
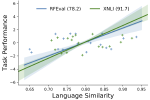
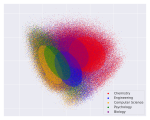
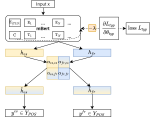
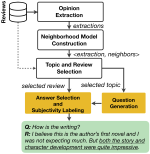
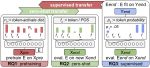
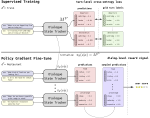
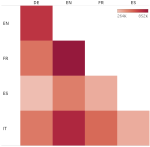
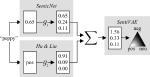
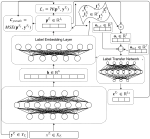
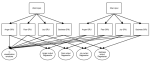
Learning with limited labelled data is useful for small domains or languages with little resources. Methods we research to mitigate problems arising in these contexts include multi-task learning, weakly supervised and zero-shot learning.
This is a cross-cutting theme in most of our research. Two previous projects specifically addressing this are Multi3Generation and Andreas Nugaard Holm’s industrial PhD project with BASE Life Science, supported by Innovation Fund Denmark.
Multi3Generation is a COST Action that funds collaboration of researchers in Europe and abroad. The project is coordinated by Isabelle Augenstein, and its goals are to study language generation using multi-task, multilingual and multi-modal signals.
Andreas Nugaard Holm’s industrial PhD project focuses on transfer learning and domain adaptation for scientific text.